before we discuss about mpox symptoms,firstly know about Mpox(Monkeypox).mpox is a viral disease caused by the monkeypox virus, which is related to smallpox. It primarily occurs in certain parts of Central and West Africa but has been reported in other regions as well. The virus is transmitted to humans through contact with infected animals, human-to-human contact, or contaminated materials.
Table of Contents
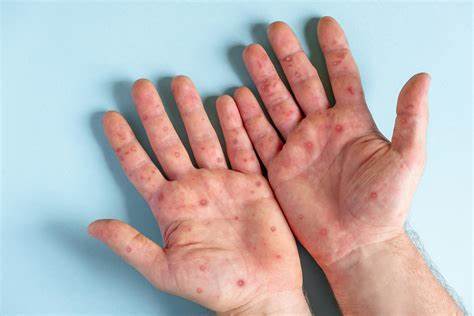
HOW TO IDENTIFY MPOX SYMPTOMS EARLY:
1. Initial Mpox Symptoms
- Fever: Often one of the first signs.
- Headache: Can be severe.
- Muscle Aches: General discomfort and pain.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: This distinguishes monkeypox from similar diseases like chickenpox.
2. Rash Development
- Appearance: The rash usually starts as flat spots (macules) and then progresses to raised bumps (papules) and fluid-filled blisters (vesicles).
- Location: The rash typically appears on the face, palms, soles of the feet, and may spread to other parts of the body.
- Stages: Lesions can crust over and eventually scab, usually taking 2 to 4 weeks to heal.
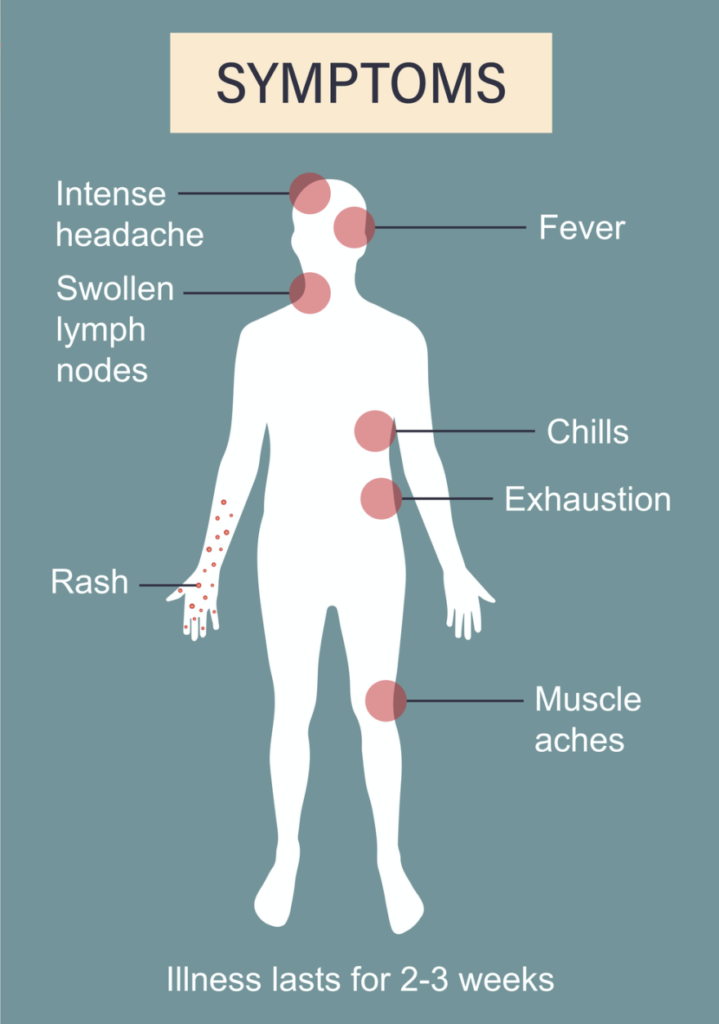
WHAT IS MONKEYPOX?
Monkeypox is a viral illness triggered by the monkeypox virus, belonging to the same family as the smallpox virus. It predominantly manifests in specific areas of Central and West Africa, although occurrences have been documented in different global locations.
HOW IT SPREADS?
- Animal to Human: The virus can be transmitted through direct contact with infected animals, such as rodents or primates.
- Human to Human: It can spread through close contact with an infected person’s bodily fluids, respiratory droplets, or contaminated materials.

DURATION AND SEVERITY
Mpox typically last 2 to 4 weeks. While monkeypox is generally less severe than smallpox, it can lead to serious complications, particularly in those with weakened immune systems.
WHO ARE IS IN HIGHLY RISK?
- Close Contacts: Individuals who have close physical contact with someone infected with monkeypox, such as family members or caregivers.
- Healthcare Workers: Those working in healthcare settings, especially without proper protective equipment, are at increased risk.
- Travelers: People traveling to regions where monkeypox is endemic (mainly Central and West Africa) may be at higher risk.
- Individuals with Weakened Immune Systems: People with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing immunosuppressive treatments, are more vulnerable to severe illness.
- Young Children: Children, particularly those under the age of 8, may be at a higher risk for severe disease.
- People in Endemic Areas: Individuals who handle or come into contact with infected animals, such as certain rodents or primates, are at risk.
- Individuals Engaging in Certain Behaviors: Those who have multiple sexual partners or engage in intimate contact with others can also be at increased risk during outbreaks.
RECENT OUTBREAKS
Global Context (2022-2023)
- 2022 Outbreak: A significant rise in cases was reported in various countries, including the United States, European nations, and parts of Africa. Many cases were linked to international travel and close contact within communities.
- Public Health Response: Health authorities implemented vaccination campaigns, particularly for high-risk populations, and increased awareness about transmission and symptoms.
Specific Regions
- United States: The U.S. saw thousands of cases during the 2022 outbreak. Public health campaigns emphasized vaccination and education about risk factors.
- Europe: Several countries reported substantial cases, leading to coordinated public health efforts.
- Africa: Endemic regions continued to report cases, particularly in Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo, where the virus has been present historically.
- India: The first confirmed Mpox symptoms in India was reported in July 2022. This case was identified in Kerala, involving a person who had traveled to the Middle East. Following this initial case, there were additional cases reported in other states, leading to increased public health measures and monitoring across the country,a few more cases were reported in other states, including Delhi and Uttarakhand.
PREVENTION ADVISE
Avoiding Contact:
- Maintain physical distance from individuals who are sick or showing symptoms.Avoid crowded places, especially during outbreaks
- Avoid contact with wild animals, particularly in areas where diseases are endemic.
- Ensure pets are vaccinated and monitored for any signs of illness.
Travel Precautions:
- Stay informed about health advisories when traveling to areas with outbreaks.
- Avoid contact with local wildlife and adhere to local health guidelines.
Health Monitoring:
- Be vigilant about your health and seek medical advice if you exhibit symptoms or have been in contact with someone infected.
- Follow any quarantine or isolation recommendations if exposed.

GOOD HYGIENE PRACTICES
Hand Hygiene
- Frequent Handwashing:
- Wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after being in public places, after coughing or sneezing, and before eating.
- Use hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol when soap and water aren’t available.
- Avoid Touching Face:
- Try not to touch your eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands.
Respiratory Hygiene
- Cover Coughs and Sneezes:
- Use a tissue or your elbow to cover your mouth and nose. Dispose of tissues immediately.
- Wear a mask if recommended, especially in crowded or enclosed spaces.
Surface Hygiene
- Disinfect Frequently Touched Surfaces:
- Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces such as doorknobs, light switches, phones, and countertops.
- Use EPA-approved disinfectants effective against viruses.
Personal Items
- Limit Sharing Personal Items:
- Avoid sharing items like utensils, towels, and personal electronics.
- Keep your belongings clean and separate from others.
Food Safety
- Practice Safe Food Handling:
- Wash fruits and vegetables before consumption.
- Ensure that food is cooked to appropriate temperatures.
Health Monitoring
- Stay Informed:
- Keep up with health guidelines from local authorities and adjust your hygiene practices as necessary.
- Monitor your health and seek medical advice if you develop symptoms
PUBLIC HEALTH INITIATIVES
1. Surveillance and Monitoring
- Case Detection: Health organizations actively monitor for suspected and confirmed cases to identify outbreaks quickly.
- Data Collection: Regular data collection helps track the spread of the virus and assess the effectiveness of interventions.
2. Public Awareness Campaigns
- Education: Informing the public about monkeypox symptoms, transmission methods, and preventive measures through media campaigns.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in education efforts to promote understanding and reduce stigma.
3. Vaccination Efforts
- Targeted Vaccination: Offering vaccines to high-risk groups, such as healthcare workers and close contacts of confirmed cases.
- Stockpiling Vaccines: Ensuring availability of vaccines for quick deployment in response to outbreaks.
4. Contact Tracing and Isolation
- Tracing Contacts: Identifying and monitoring individuals who may have been exposed to infected persons.
- Isolation Protocols: Implementing isolation for confirmed cases to prevent further transmission.
5. Collaboration with International Organizations
- Partnerships: Collaborating with the World Health Organization (WHO) and other international bodies for guidance, resources, and best practices.
- Global Reporting: Sharing data and insights with global health networks to improve response strategies.
6. Research and Development
- Ongoing Research: Supporting studies to better understand the virus, its transmission, and potential treatments.
- Clinical Trials: Encouraging trials for vaccines and antiviral medications specific to monkeypox.
7. Healthcare Provider Training
- Training Programs: Providing training for healthcare professionals on recognizing symptoms and managing cases.
- Guidelines: Issuing protocols for infection control in healthcare settings.
CONCLUSION
Mpox symptoms may cause worry, particularly for those with compromised immune systems. It is crucial to take precautions to prevent contracting the virus. First, limit exposure to infected individuals or animals. Second, follow travel advisories diligently, particularly in areas experiencing outbreaks. Lastly, monitor your health closely for any indications or symptoms. Stay safe by prioritizing proper hygiene practices, including hand hygiene, respiratory hygiene, and surface hygiene.
SEE HOW NIPAH VIRUS IS SPREADING IN KERALA
WANT TO KNOW ABOUT HOW TO IMPROVE IMMUNE SYSTEMS?.THEN CLICK ON THIS LINK
